Cannabis, the Future of Autoimmune Disorders
India is moving towards clinical trials of cannabis to establish medical evidence and there are potential ways to bring a regulated regime of medicinal cannabis in place. A number of countries have legalised medicinal cannabis and are tapping the potential aspect of cannabis economy.
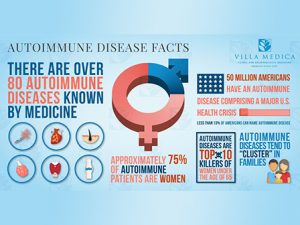
More and more researches have been showing the medical evidence of cannabis to treat many  diseases. The Autoimmune disorders (AIDs) is one among them. AIDs occur when the body’s immune system loses the ability to differentiate between foreign cells and the body’s own cells. As a consequence, the antibodies produced start attacking its own cells instead of fighting against foreign bodies. A famous example of an autoimmune disorder is Type 1 Diabetes, which affects only one organ – the pancreas. While other disorders such as the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus or SLE go on to affect multiple tissues and organs. Other widespread autoimmune disorders include Multiple Sclerosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, psoriasis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.
diseases. The Autoimmune disorders (AIDs) is one among them. AIDs occur when the body’s immune system loses the ability to differentiate between foreign cells and the body’s own cells. As a consequence, the antibodies produced start attacking its own cells instead of fighting against foreign bodies. A famous example of an autoimmune disorder is Type 1 Diabetes, which affects only one organ – the pancreas. While other disorders such as the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus or SLE go on to affect multiple tissues and organs. Other widespread autoimmune disorders include Multiple Sclerosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, psoriasis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.
Although the exact causes of an autoimmune disorder are still unknown, research suggests that they could be genetic, environmental, or both. According to the Journal of Immunology Research, the genetic factors and the environmental factors are likely interwoven and together entail what is popularly known as ‘epigenetics.’ Currently, studies show that genetic factors account for only 30 percent of the autoimmune disorders while the remaining 70 percent are due to environmental factors. Since women are more prone to these disorders than men, scientists conjecture that hormones might also play a role in it.
There is no specific data on the number of people suffering with autoimmune disorders in India, but globally an estimate of 700 million people are said to be affected by these disorders.
Also Read : Seek Drug Reform Within International Law Tom blickman
Broadly speaking, people suffering from such disorders alternately experience phases of flare-ups(i.e., when the symptoms are highly aggravated),followed by phases of remission (or temporary relief). Most AIDs patients have similar symptoms making it difficult to distinguish between the disorders. But some common symptoms are fever, fatigue, general malaise, joint and muscular pain, weight loss, insomnia, etc. Most common line of treatment followed is to suppress the activity of the immune system which is done by taking anti-inflammatory medicines or steroids. However, this method only provides temporary relief to the patients as it suppresses the symptoms for some time and does not cure it completely.
A promising avenue in this field has been the discovery and study of cannabis and its components (especially THC, CBD and the cannabinoid receptors) in the 20th century that has led to an increase in research of cannabis for medicinal purposes.
For the past several centuries cannabis had been mostly used for recreational purposes as marijuana or hashish due to its psychoactive component, the THC (delta-9-tetra hydro cannabinol). With further research, it was found that the secretions of the cannabis plants or simply the “cannabinoids”, possessed therapeutic properties. The cannabinoids such as THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) or CBD (cannabidiol) bind with the cannabinoid receptors of our body (CB1 and CB2) and cause changes to it. The CB1 receptors are primarily found in the nervous system, the spinal cord and other tissues and organs and the CB2 receptors in the immune system and the gastrointestinal tract. The CB1 receptors help in reducing pain, nausea, and regulate motor controls and transmission of the neurotransmitters while the CB2 receptors help in the working of the immune system and its functions. The CB2 receptorsso play a role in regulating appetite and lessening pain. However, one of the most crucial roles played by CB2 receptors is regulating the cytokine release which has anti-inflammatory properties and comprises a key immune response.
 Research has proved that cannabis can act as an analgesic and shows antiemeticroperty (helps in easing nausea or vomiting) which has been useful for relieving patients undergoing cancer chemotherapy, of nausea and vomiting. A study in 2016 showed that CBD and THC decreased glucose levels and increased insulin levels in the blood, helping in glycemic control, i.e., curing Type 1 Diabetes.
Research has proved that cannabis can act as an analgesic and shows antiemeticroperty (helps in easing nausea or vomiting) which has been useful for relieving patients undergoing cancer chemotherapy, of nausea and vomiting. A study in 2016 showed that CBD and THC decreased glucose levels and increased insulin levels in the blood, helping in glycemic control, i.e., curing Type 1 Diabetes.
A placebo-controlled trial was carried out in 2014 on 21 patients suffering with Crohn’s disease (an inflammatory bowel autoimmune disorder). Eleven of these patients were given cannabinoids out of which 5 showed complete remission and the others showed massive improvement in their conditions. While the remaining 10 patients were given the placebo, out of which only 4 showed minor improvements in their conditions. These studies demonstrated that cannabinoids have anti-inflammatory properties that bring about a decrease in the level of inflammatory proteins, i.e., the cytokines in the body. Type 1 Diabetes, Crohn’s, Ulcerative Colitis and other inflammatory diseases are being treated by utilizing this property of the cannabinoids.
Also Read : Negative Perception Surrounds Opium Farming Says Mp Sudheer Gupta
However, this field of research is not without its share of complications, majority of which centre around the legal, ethical and societal issues concerning the safety and toxicity of marijuana use for medicinal purposes. Its classification as a Schedule I drug has led to a slow down in further research as scientists are required to possess a special license to study it and due to this reason, cannabis and its derivatives have not been successfully developed into medicine despite its potential as a therapeutic agent.
Canada became the first country to legalise medicinal cannabis in the year 2001, followed by Austria in 2008.
Many countries like Argentina, Croatia, Italy, New Zealand, Thailand, Uruguay and Jamaica have also legalised medicinal cannabis. In the United States, California became the first state to legalise marijuana for medicinal purposes, in the year 1996. Today, about 33 states of the USA have amended their state laws regarding the same. DPA or the Drug Policy Alliance is a non-profit organisation which is working towards the legalisation of marijuana for medicinal purposes at both the state and federal levels in the US.
India, where ‘Bhang’ is the only form of cannabis that is legalised for recreational purposes, is yet to work and legalise medicinal cannabis. Promisingly, in 2016, CSIR-IIMC started its research on development of cannabis-based medicines for treating various diseases such as epilepsy, anaemia and cancer. Now, several other nations are petitioning to permit the cultivation of cannabis for medicinal purposes. This would not only prove beneficial for curing of these disorders but also add to the economy of the country by improving the agricultural aspects and increasing job opportunities.
With the approval of the Food and Drug Administration, a federal agency of the United States, the first Cannabis-derived (CBD) drug, Epidiolex was developed, and two severe and rare forms of Epilepsy are being treated, and the other synthetic medicines, Cesamet and Nabilone, are being used to treat the after-effects of chemotherapy and anorexia, respectively. Similarly, the availability of CBD oil in some countries is helping in healing of these autoimmune disorders. Thus it might be safe to say that medicinal cannabis can be used to alleviate pain and sufferings and that with further research it can pave a new path to curing several autoimmune disorders.
